Introduction
CERTs such as CIRCL and security teams collect and process content such as images (at large from photos, screenshots of websites or screenshots of sandboxes). Datasets become larger - e.g. on average 10000 screenshots of onion domains websites are scrapped each day in AIL - Analysis Information Leak framework, an analysis tool of information leak - and analysts need to classify, search and correlate through all the images.
Automatic tools can help them in this task. Less research about image matching and image classification seems to have been conducted exclusively on websites screenshots. However, a classification of this kind of pictures needs to be addressed.
Goal
Image-matching algorithms benchmarks already exist and are highly informative, but none is delivered turnkey.
Our long-term objective is to build a generic library and services which can at least be easily integrated in Threat Intelligence tools such as AIL, and MISP - Malware Information Sharing Platform. A quick-lookup mechanism for correlation would be necessary and part of this library. This paper includes the release of two datasets to support research effort in this direction.
MISP is an open source software solution tool developed at CIRCL for collecting, storing, distributing and sharing cyber security indicators and threats about cyber security incidents analysis. AIL is also an open source modular framework developed at CIRCL to analyze potential information leaks from unstructured data sources or streams. It can be used, for example, for data leak prevention.
The dataset presented on this page is strongly associated with other projects, which are an evaluation framework provided as Carl-Hauser and the open-source library provided as Douglas-Quaid.
Problem Statement
Image correlation for security event correlation purposes is nowadays mainly manual. No open-source tool provides easy correlation on pictures, without regard to the technology used. Ideally, the extraction of links or correlation between these images could be fully automated. Even partial automation would reduce the burden of this task on security teams. Datasets are part of the foundation needed to construct such tool.
Our contribution about this problem is the provision of datasets to support research effort in this direction.
Dataset description
circl-ail-dataset-01
This dataset is named circl-ail-dataset-01 and is composed of AIL’s scraped onion websites. Around 37500 pictures are in this dataset to date.
Only one label-classification (DataTurks direct output) is provided along with the dataset. This classification is per part and will be improved and updated as soon as classification operations had been achieved.
Direct link : https://www.circl.lu/opendata/datasets/circl-ail-dataset-01/
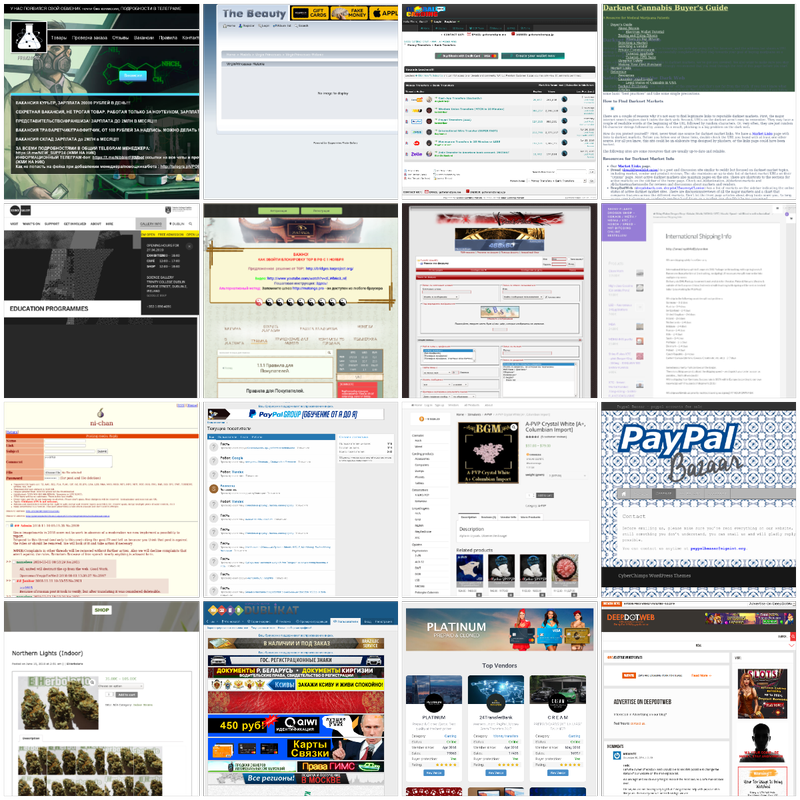
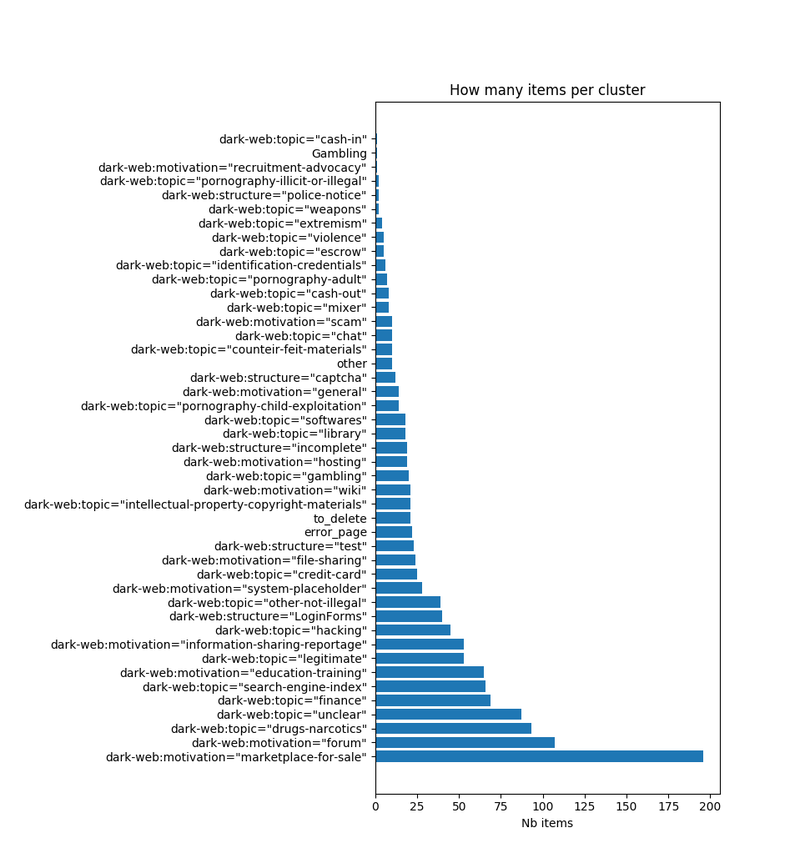
Sampled over 800 pictures
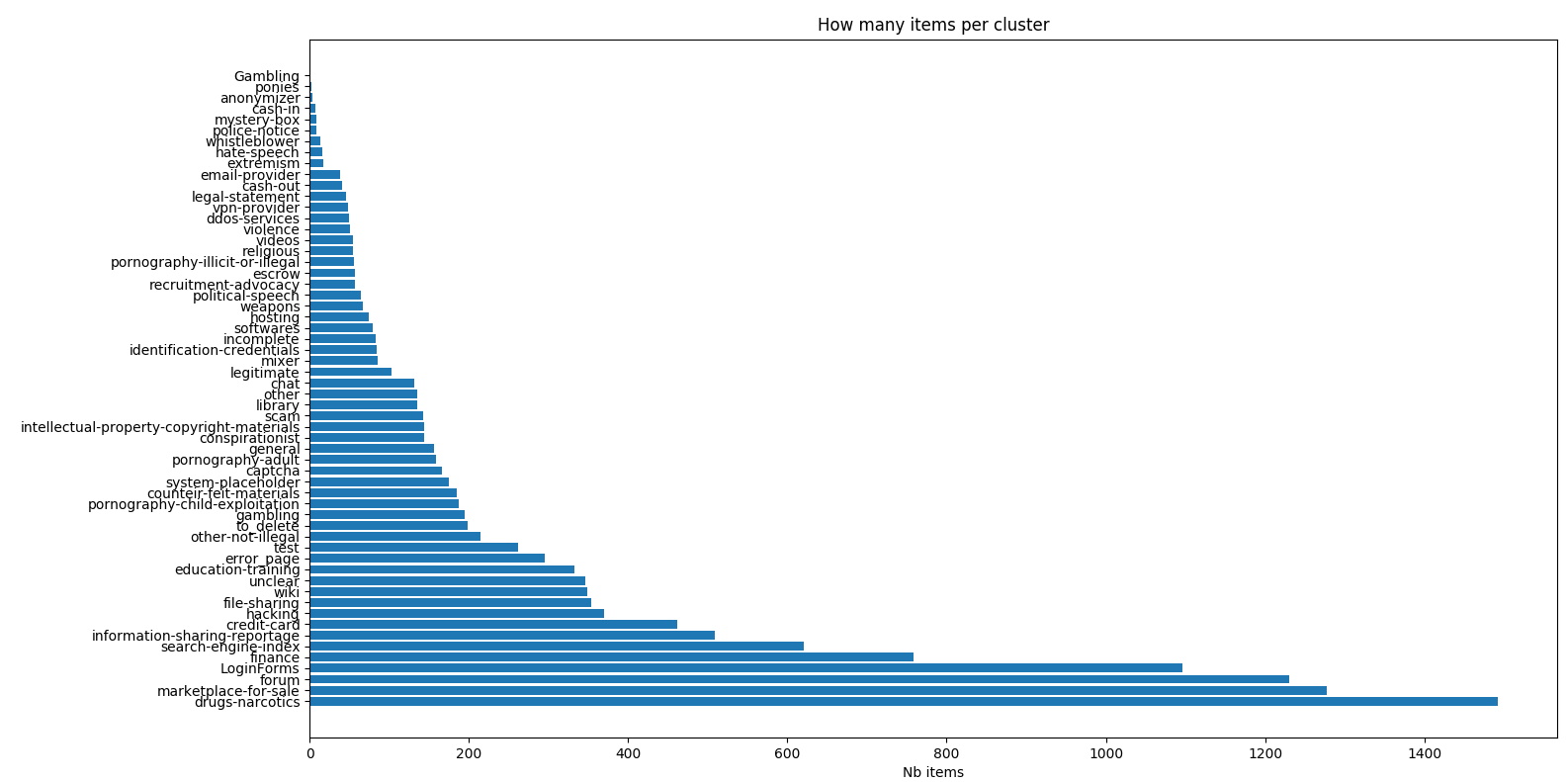
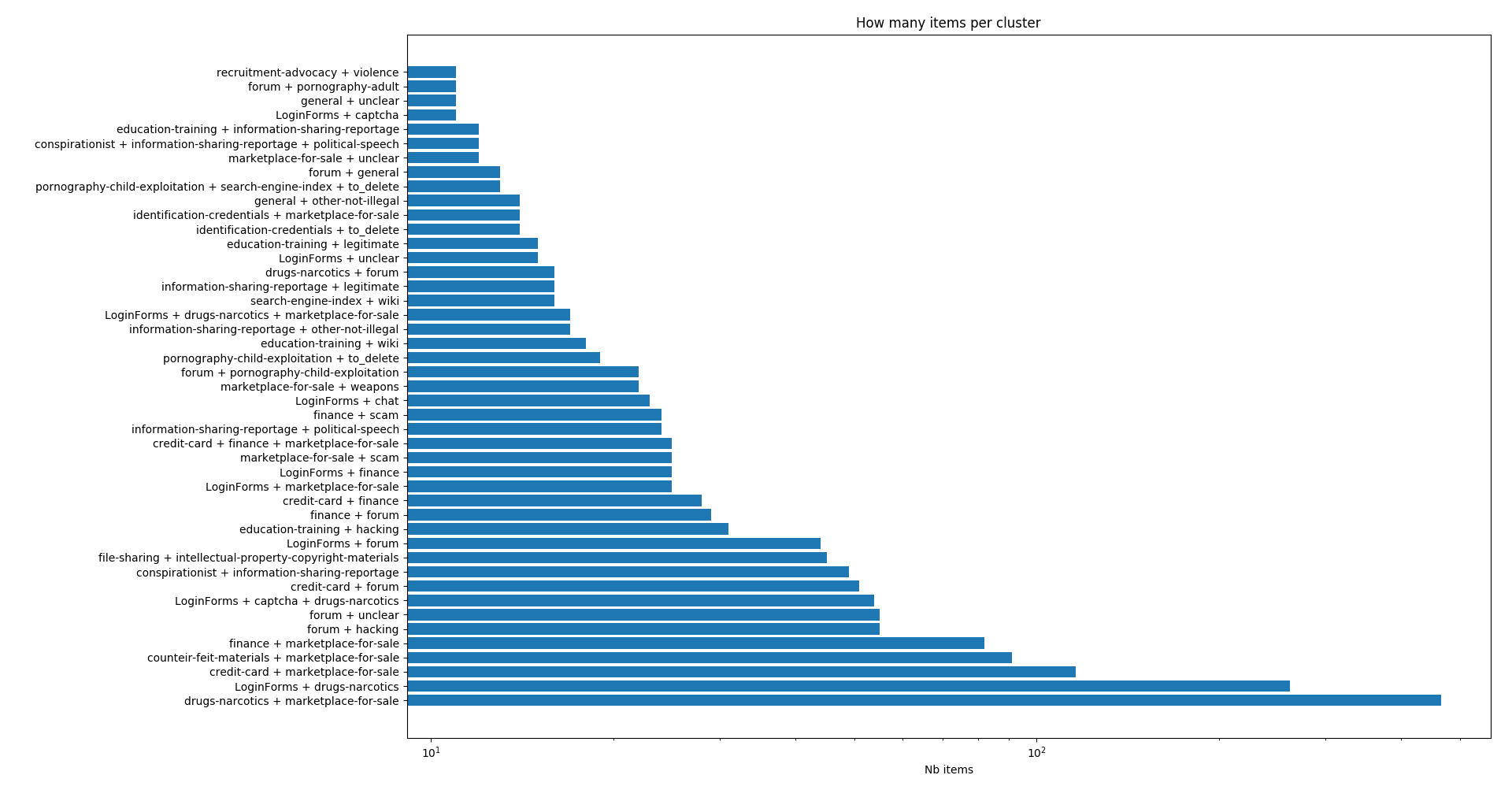
Sampled over 9500 pictures. Be aware of the log scale of the second frequency chart.
Data sources
Different tools collected the dataset presented on this page. The screenshots’s data source is a subset of onion domain websites scrapped by AIL;
Processing on datasets
Each picture’s content of each dataset was hashed to “humanly readable” name to allow a unified and readable reference system for image’s naming convention. This had been performed with a slightly modified version of Codenamize - Consistent easier-to-remember codenames generator. The bytes-content of each file is hashed and mapped to a list of words, from a dictionary.
Collision were handled by keeping track of which name has already been generated, and temporary adding bytes to each colliding file. However collision were still rare. A human-readable hash of 3 adjectives (without a maximum number of characters) can generates up to 2 trillion combinations, which is far sufficient to handle even 40 000 pictures without common collision occurrence. Collision were however easily met in case of similar pictures (typically, all white or all dark pictures) but then, their name can be swapped without incidence on the meaning of the dataset.
This dataset is a folder of pictures as well as a reference JSON, containing a mapping from file names to MD5, SHA1, SHA256 of each picture. This allows an easy retrieval of which picture is which, in case picture names need to be modified.
We manually reviewed datasets, picture by picture. We used a private instance of Dataturks - OpenSource Data Annotation tool for teams to perform classification and review the datasets. We removed datasets pictures which were identified as containing personal information such as sensitive e-mail address clearly displayed on screenshoots, … We also manually removed pictures which were identified as containing harmful content, such as violent, offensive, obscene or equivalent undesirable pictures which may shock anyone.
We makes reasonable effort not to display anything in the dataset which may specifically identify an individual. This dataset is provided for research purposes. We stay available for any request. Please refer to contact information at the end of this page. Please note that each website behind each screenshot can be freely accessed by one with relevant means.
Potential Use
These datasets can be used to create classifiers, which then can be used to automate processes. Few examples of application :
- Automatically classify onion website;
- Correlate object on pictures from crawled websites, mainly with screenshots of hidden services (AIL usecase);
- Correlate websites screenshots to cluster of websites with common topic together, to keep track of domain-name changes for example (Lookyloo usecase).
- Isolate and characterize outliers
- Extracting statistics about crawled websites (per theme, per type, per content, per access allowance …)
Detailed information of the dataset
Labels are used to classify each picture in one or more cluster. Labels are different depending on the dataset and the tool used to classify it.
AIL dataset
Pictures are labeled following MISP “dark-web” taxonomy - Taxonomies used by MISP and other information threat sharing tools.
Labels are expressed as triplets ‘namespace:predicate=value’. For example ‘dark-web:topic=”hacking”’ is one label of this taxonomy. Two labels were added : “error page” and “other” which does not specifically belongs to dark-web, but could cover any other case met in the dataset.
For a complete list of labels used, please see the following :
1dark-web:topic="drugs-narcotics", 2dark-web:topic="extremism", 3dark-web:topic="finance", 4dark-web:topic="cash-in", 5dark-web:topic="cash-out", 6dark-web:topic="hacking", 7dark-web:topic="identification-credentials", 8dark-web:topic="intellectual-property-copyright-materials", 9dark-web:topic="pornography-adult", 10dark-web:topic="pornography-child-exploitation", 11dark-web:topic="pornography-illicit-or-illegal", 12dark-web:topic="search-engine-index", 13dark-web:topic="unclear", 14dark-web:topic="violence", 15dark-web:topic="weapons", 16dark-web:topic="credit-card", 17dark-web:topic="counteir-feit-materials", 18dark-web:topic="gambling", 19dark-web:topic="library", 20dark-web:topic="other-not-illegal", 21dark-web:topic="legitimate", 22dark-web:topic="chat", 23dark-web:topic="mixer", 24dark-web:topic="mystery-box", 25dark-web:topic="anonymizer", 26dark-web:topic="vpn-provider", 27dark-web:topic="email-provider", 28dark-web:topic="escrow", 29dark-web:topic="softwares", 30dark-web:motivation="education-training", 31dark-web:motivation="file-sharing", 32dark-web:motivation="forum", 33dark-web:motivation="wiki", 34dark-web:motivation="hosting", 35dark-web:motivation="general", 36dark-web:motivation="information-sharing-reportage", 37dark-web:motivation="marketplace-for-sale", 38dark-web:motivation="recruitment-advocacy", 39dark-web:motivation="system-placeholder", 40dark-web:motivation="conspirationist", 41dark-web:motivation="scam", 42dark-web:motivation="hate-speech", 43dark-web:motivation="religious", 44dark-web:structure="incomplete", 45dark-web:structure="captcha", 46dark-web:structure="LoginForms", 47dark-web:structure="police-notice", 48dark-web:structure="test", 49dark-web:structure="legal-statement", 50error_page, 51other,
Clustering file format for Dataturks tool is a list of filename along with their labels, to which they belong. Here follows technical overview of this file format:
Future work
This lead to a list of future possible developments :
- Extending provided dataset to support research effort
- Improve classification provided
- Add images extracted from DOM. These pictures allow a more particular matching.
Please note that ground truth files provided with current dataset as well as dataset themselves may evolve and be updated.
Even partial automation of screenshots classification would reduce the burden on security teams, and that the data we provide is a step further in this direction.
FAQ
Questions have emerged since the discussions about the published datasets.
Is the frequency of appearance of all labels representing reality?
Label frequencies were calculated on a sample of the original dataset and measured before removal of any offensive images. The statistics of the initial data set and the downloadable data set are therefore different. Some labels require explanations, which can be found in the MISP-darkweb taxonomy.
For example, the label “other-not-illegal” refers to any image that does not fall into any other obvious category and is not potentially illegal. The “legitimate” label refers to personal websites, blogs on general content, etc. The “other-not-illegal” label can for example refer to Tor Wiki (also labelled as “wiki”), websites that allow you to perform calculations online (e.g. hashing tools, calculator) or online gaming sites (without money).
“Finance” is a very broad category referring to many subtypes: “Crypto currency”, “Pump and dump”, “Mixers”, “Credit-Card sellers”, “Paypal-related” schemes, “CryptoWallets”, “Escrows”, which may or may not be represented by other labels. Market-Places are usually not labelled as “Finance”.
Is it really useful to know the frequency of labels?
We can only recommend calculating the frequency of label sets. The frequency of the X or Y label is not as interesting as the frequency of a set of labels.
Images can have multiple labels. Thus, the number of sites labelled “Forum + Drugs + Finance” compared to the number of sites labelled “Market-Places + Weapons” provides more information than the overall frequency of the “Finance” label alone.
What is the legality of these data sets?
The answer has several points. In context of GDPR, the dataset is part of a scientific publication for scientific purposes. Although GDPR has a clause for this particular case, we have manually reviewed the data sets to avoid diffusion of personal information leaks (DOX). Elements may have been missed by us, so we remain available for any comments regarding these datasets. Regarding the legal aspects of the collection, all data sources are freely available with sufficient means of access. Crawling is basic and does not involve exploiting vulnerabilities, for example. Regarding the aspects related to crawling offensive content, we work closely with the relevant authorities in the fight against the dissemination of such content.
Can these datasets be used as a links index?
We have revised the dataset to remove explicit links (clearly readable and copyable) to websites that share offensive content. Thus,”.onion” addresses clearly pointing to offensive content were removed from the datasets.
Do I need psychological support to use this dataset?
The data sets available for downloading do not contain offensive content. They can be downloaded, viewed and used by the majority of audiences, especially those with a Western/Western European reference system. This dataset could even be used for educational purposes to show (in a watered-down way) - even if we don’t recommend it - what is present on the dark-web. Content culturally unacceptable is understood in the standards of the Western and Western European countries reference system.
Is everything in this dataset true?
As true as what it represents. These sites do exist, but what they offer can be scam. We have not done any tests in this regard. As a rule of thumb, most “Finance” or “Market-Place” websites are probably scam. A “scam” label exists, and only the websites presenting the most obvious scams have been labelled as such. In particular, market places for high-tech products (e.g. iPhone) are generally scam.
What does the label “Religious” refer to?
In general, sites offering Bible excerpts, or discussions about religion are labelled as such. Very little content related to sects or equivalent is present in the data set.
Is the dataset “classified” as “secret” or “labelled”?
The dataset is labelled and public.
Links
- Complete dataset https://www.circl.lu/opendata/datasets/circl-ail-dataset-01/
- State-of-The-Art - Carl Hauser https://github.com/CIRCL/carl-hauser/blob/master/SOTA/SOTA.md
- Open Source implementation - Douglas Quaid https://github.com/CIRCL/douglas-quaid
- AIL framework - Analysis Information Leak framework - https://github.com/ail-project/ail-framework
Contact information
If you have a complaint related to the dataset or the processing over it, please contact us. We aim to be transparent, not only about how we process but also about rights that are linked to such information and processing.
You can contact us at circl.lu/contact/ for request about the dataset itself, regarding elements of the dataset, or extension requests. You can contact us at same address or on github for feedback about the benchmarking framework, methodology or relevant ideas/inquiries.
Cite
@Electronic{CIRCL-AILDS2019,
author = {Vincent Falconieri},
month = {07},
year = {2019},
title = {CIRCL Images AIL Dataset},
organization = {CIRCL},
address = {CIRCL - Computer Incident Response Center Luxembourg c/o "security made in Lëtzebuerg" (SMILE) g.i.e. 122, rue Adolphe Fischer L-1521 Luxembourg Grand-Duchy of Luxembourg},
url = {https://www.circl.lu/opendata/circl-ail-dataset-01/},
abstract = {This dataset is named circl-ail-dataset-01 and is composed of Tor hidden services websites screenshots. Around 37000+ pictures are in this dataset to date.},
}
Revision
- Version 1.0 - 2019-07-10 (initial release)